Neurotransmitter Gamma-aminobutyric Acid Function
-
Table of Contents
- Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA): Understanding Its Crucial Role in the Brain
- What is Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid?
- The Mechanism of GABA Function
- Roles of GABA in the Brain
- GABA’s Role in Health and Disease
- Epilepsy and Seizure Disorders
- Anxiety Disorders
- Depression
- Insomnia
- Research and Future Directions
- Conclusion: The Significance of GABA in Brain Function
- Discover the Benefits of ETprotein’s Protein Products
Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA): Understanding Its Crucial Role in the Brain
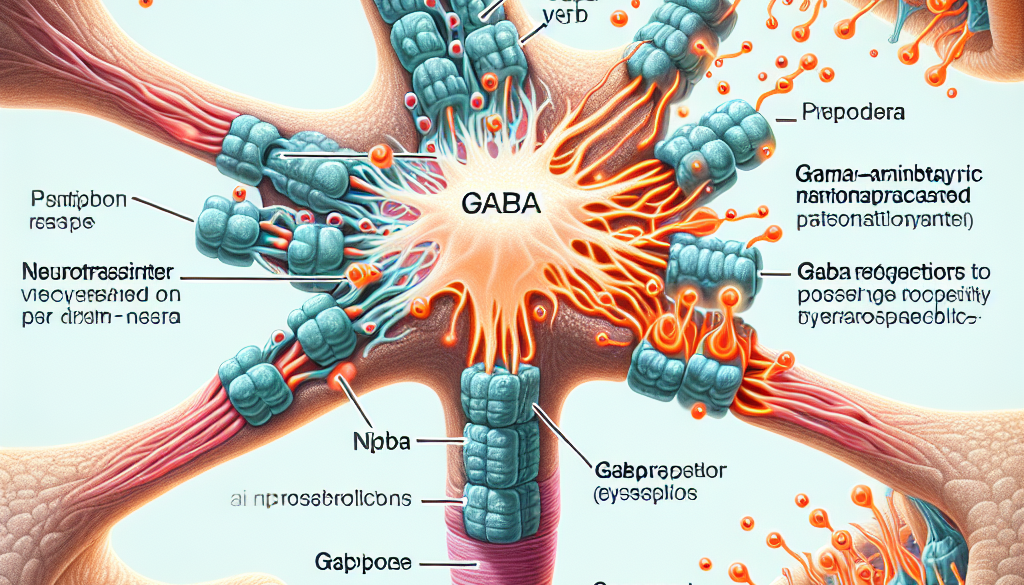
Gamma-aminobutyric acid, commonly known as GABA, is a neurotransmitter that plays a pivotal role in regulating brain function and maintaining mental health. As the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, GABA is essential for balancing neural activity and preventing overexcitation. This article delves into the complex world of GABA, exploring its functions, mechanisms, and implications for health and disease.
What is Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid?
GABA is a naturally occurring amino acid that functions as a neurotransmitter in the brain. It is synthesized from glutamate, another neurotransmitter, through the action of the enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD). GABA’s primary role is to inhibit the firing of neurons, which helps to regulate neural activity and maintain a balance between excitation and inhibition in the nervous system.
The Mechanism of GABA Function
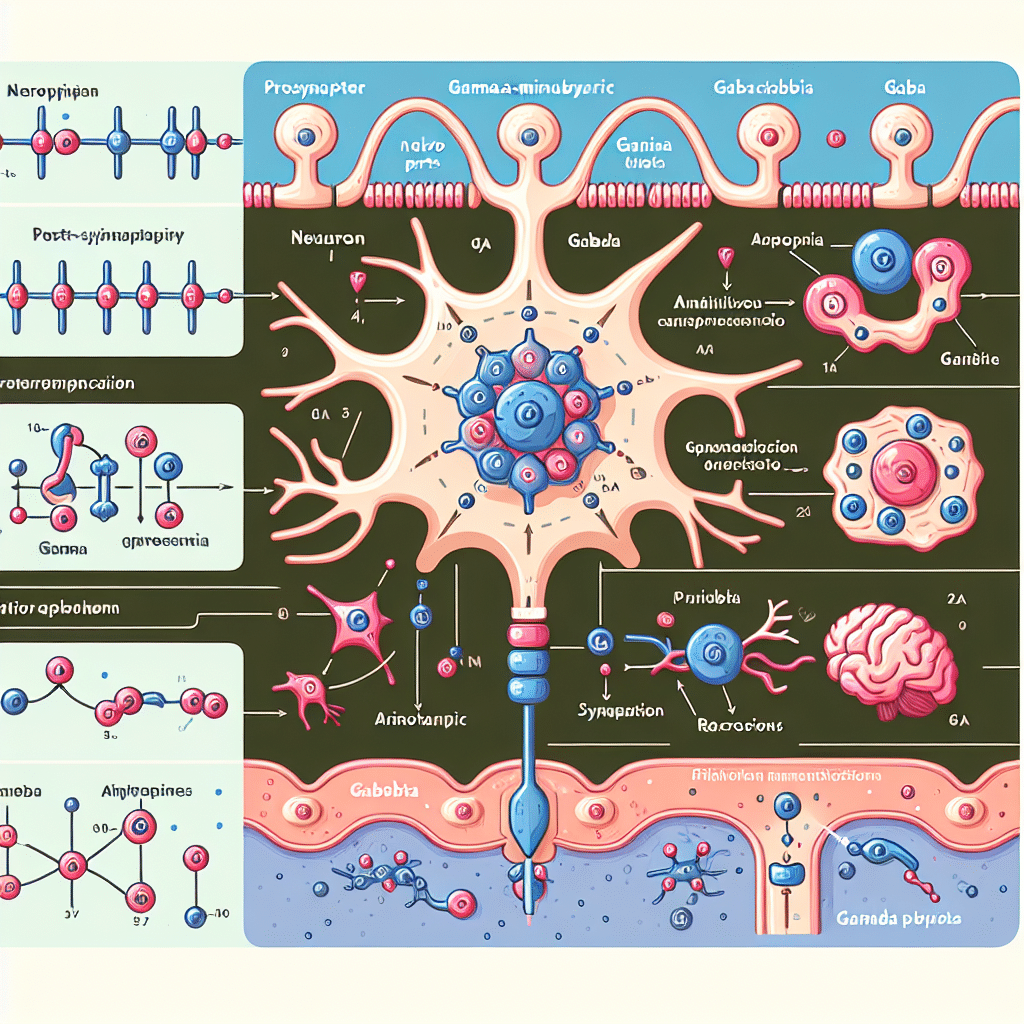
GABA exerts its effects by binding to specific receptors on the surface of neurons. There are two main types of GABA receptors: GABAA and GABAB. GABAA receptors are ionotropic, meaning they form ion channels that open upon receptor activation, allowing chloride ions to flow into the neuron and hyperpolarize it, making it less likely to fire. GABAB receptors are metabotropic, which means they activate second messenger systems that can have a variety of effects on the neuron, including opening potassium channels to hyperpolarize the neuron or inhibiting calcium channels to reduce neurotransmitter release.
Roles of GABA in the Brain
- Regulation of Neural Excitability: By inhibiting neural activity, GABA helps prevent excessive firing that can lead to seizures and other neurological disorders.
- Modulation of Sleep: GABA activity increases during sleep, particularly during the deep stages, suggesting a role in sleep regulation and the sleep-wake cycle.
- Anxiety and Stress Reduction: GABAergic neurons are involved in the brain’s response to stress and anxiety, with GABA acting to calm the nervous system.
- Motor Control: GABA is involved in controlling muscle tone and movement, with imbalances potentially leading to conditions such as spasticity.
- Cognitive Functions: GABA plays a role in shaping learning and memory by influencing synaptic plasticity and the formation of neural circuits.
GABA’s Role in Health and Disease
Given its central role in neural regulation, GABA is implicated in a variety of health conditions and diseases. Disorders such as epilepsy, anxiety, depression, and insomnia have been linked to disruptions in GABAergic signaling. Research into these conditions often focuses on how to modulate GABA levels or receptor activity to restore balance and alleviate symptoms.
Epilepsy and Seizure Disorders
Epilepsy is characterized by recurrent seizures, which are often the result of excessive neural excitation. Medications that enhance GABAergic activity, such as benzodiazepines and barbiturates, are commonly used to treat seizure disorders by increasing the inhibitory effects of GABA and reducing neuronal excitability.
Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders are associated with decreased GABAergic function. Anxiolytic drugs, such as benzodiazepines, work by enhancing the effects of GABA, providing rapid relief from anxiety symptoms. However, these medications can be addictive and are typically prescribed for short-term use.
Depression
Depression has also been linked to altered GABAergic signaling. Some studies suggest that depressed individuals have reduced levels of GABA in certain brain regions. While traditional antidepressants primarily target the serotonin and norepinephrine systems, there is growing interest in developing treatments that modulate GABAergic neurotransmission.
Insomnia
Insomnia and other sleep disorders may be related to disruptions in GABA levels. GABAergic drugs, such as certain types of sleeping pills, can increase GABA activity and promote sleep. However, like anxiolytics, these medications can have side effects and risks associated with long-term use.
Research and Future Directions
Research into GABA continues to uncover its complexities and potential therapeutic applications. Novel treatments for neurological and psychiatric disorders are being explored, including drugs that target GABA receptors more selectively to minimize side effects. Additionally, natural interventions, such as dietary changes, exercise, and stress-reduction techniques, are being studied for their potential to influence GABAergic function and improve mental health.
Conclusion: The Significance of GABA in Brain Function
In summary, GABA is a fundamental neurotransmitter that plays a critical role in maintaining the delicate balance of neural activity in the brain. Its functions are diverse, influencing everything from sleep and relaxation to cognition and motor control. Disruptions in GABAergic signaling are implicated in a range of neurological and psychiatric disorders, making it a key target for research and treatment development. Understanding GABA’s intricate mechanisms continues to be a vital area of study with the potential to yield significant advances in mental health care.
Discover the Benefits of ETprotein’s Protein Products
For those interested in supporting their overall health and well-being, ETprotein offers a range of high-quality protein products. Their offerings include organic rice protein, pea protein, and various seed proteins, all characterized by a neutral taste and non-GMO, allergen-free attributes. With L-(+)-Ergothioneine purity over 98%, ETprotein’s products cater to diverse industries, including nutraceuticals, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverage. To explore how these protein products can benefit your health regimen, contact ETprotein and sample their products today.
About ETprotein:
ETprotein, a reputable protein and L-(+)-Ergothioneine (EGT) Chinese factory manufacturer and supplier, is renowned for producing, stocking, exporting, and delivering the highest quality organic bulk vegan proteins and L-(+)-Ergothioneine. They include Organic rice protein, clear rice protein, pea protein, clear pea protein, watermelon seed protein, pumpkin seed protein, sunflower seed protein, mung bean protein, peanut protein, and L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT Pharmaceutical grade, L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT food grade, L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT cosmetic grade, L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT reference grade and L-(+)-Ergothioneine EGT standard. Their offerings, characterized by a neutral taste, non-GMO, allergen-free attributes, with L-(+)-Ergothioneine purity over 98%, 99%, cater to a diverse range of industries. They serve nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, cosmeceutical, veterinary, as well as food and beverage finished product distributors, traders, and manufacturers across Europe, USA, Canada, Australia, Thailand, Japan, Korea, Brazil, and Chile, among others.
ETprotein specialization includes exporting and delivering tailor-made protein powder and finished nutritional supplements. Their extensive product range covers sectors like Food and Beverage, Sports Nutrition, Weight Management, Dietary Supplements, Health and Wellness Products, and Infant Formula, ensuring comprehensive solutions to meet all your protein needs.
As a trusted company by leading global food and beverage brands and Fortune 500 companies, ETprotein reinforces China’s reputation in the global arena. For more information or to sample their products, please contact them and email sales(at)ETprotein.com today.